When bonding two pieces of metal, either the metals must melt a bit where they meet or some molten metal must be introduced between the pieces. A solid bond then forms when the metal solidifies again. But researchers at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) have found that, in some situations, melting can actually inhibit metal bonding rather than promote it.
This surprising and counterintuitive finding could have serious implications for the design of certain coating processes or for 3D printing, which both require getting materials to stick together and stay that way. The research, carried out by postdocs Mostafa Hassani-Gangaraj and David Veysset and professors Keith Nelson and Christopher Schuh, is reported in two papers in Physical Review Letters and Scripta Materialia.
Schuh, who is professor of metallurgy and head of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, explains that one of the papers outlines "a revolutionary advance in the technology" for observing extremely high-speed interactions, while the other makes use of that high-speed imaging to reveal that melting induced by impacting metal particles can impede bonding.
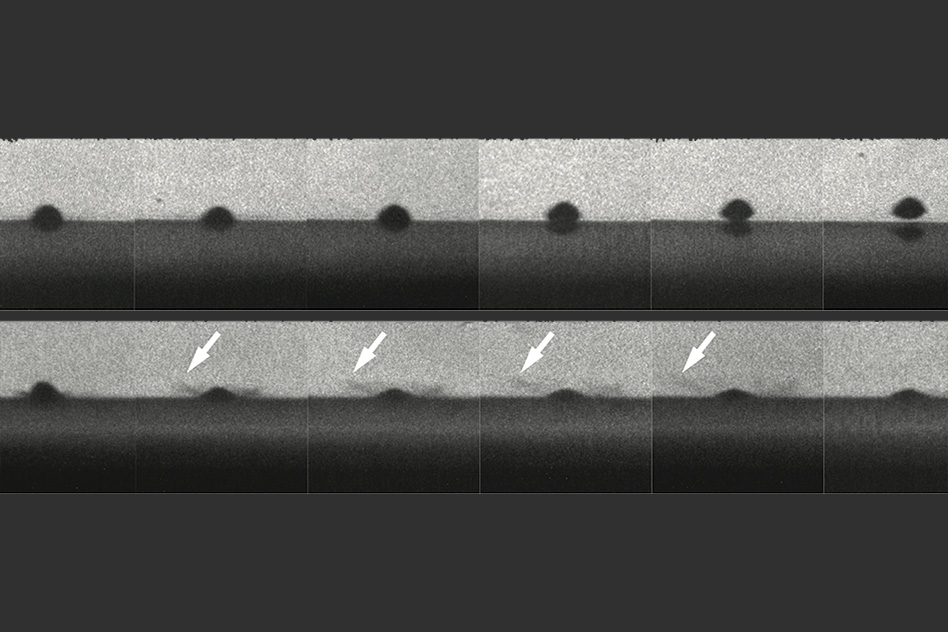
The optical setup, with a high-speed camera that uses 16 separate charged-coupled device (CCD) imaging chips and can record images in just 3 nanoseconds, was primarily developed by Veysset. The camera is so fast that it can track individual particles being sprayed onto a surface at supersonic velocities, a feat that was previously not possible. The team used this camera, which can shoot up to 300 million frames per second, to observe a spray-painting-like process similar to ones used to apply a metallic coating to surfaces in many industries.
While such processes are widely used, until now their characteristics have been determined empirically, since the process itself is so fast "you can't see it, you can't tell what's happening, and no one has ever been able to watch the moment when a particle impacts and sticks," Schuh says. As a result, there has been ongoing controversy about whether the metal particles actually melt as they strike the surface to be coated. The new technology means that now the researchers "can watch what's happening, can study it, and can do science," he says.
The new images make it clear that, under some conditions, the particles of metal being sprayed at a surface really do melt the surface – and that, unexpectedly, prevents them from sticking. The researchers found that the particles bounce away in much less time than it takes for the surface to re-solidify, so they leave the surface while it is still molten.
If engineers find that a coating material isn't bonding well, they may be inclined to increase the spray velocity or temperature in order to increase the chances of melting. However, the new results show the opposite: melting should be avoided.
It turns out the best bonding happens when the impacting particles and impacted surfaces remain in a solid state but ‘splash’ outward in a way that looks like liquid. It was "an eye-opening observation," according to Schuh. This phenomenon "is found in a variety of these metal-processing methods," he says. Now, it is clear that "to stick metal to metal, we need to make a splash without liquid. A solid splash sticks, and a liquid one doesn't." With the new ability to observe the process, Hassani-Gangaraj says, "by precise measurements, we could find the conditions needed to induce that bond."
The findings could be relevant for processes used to coat engine components in order to reuse worn parts rather than relegating them to the scrap-metal bin. "With an old engine from a large earth-moving machine, it costs a fortune to throw it away, and it costs a fortune to melt and recast it," Schuh says. "Instead, you can clean it off and use a spray process to renew the surface." But that requires that the sprayed coating remains securely bonded.
In addition to coatings, the new information could also help in the design of some metal-based additive manufacturing systems, also known as 3D printing. There, as with coatings, it is critical to make sure that one layer of the printing material adheres solidly to the previous layer.
"What this work promises is an accurate and mathematical approach" to determining the optimal conditions to ensure a solid bond, Schuh says. "It's mathematical rather than empirical."
This story is adapted from material from MIT, with editorial changes made by Materials Today. The views expressed in this article do not necessarily represent those of Elsevier. Link to original source.



