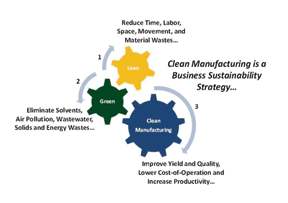




In an environment of escalating manufacturing challenges—including intense global competitiveness, environmental regulation and energy supply issues—managers must have both lean and green manufacturing (a.k.a “clean manufacturing”) technology necessary to identify and eliminate multifaceted manufacturing wastes in their operations that stealthily steal away business profits. CO2 CleanTech represents a significant business opportunity for those manufacturers that can adapt their production tools and operations to meet the new challenges ahead. Moreover, the merging of green practices into manufacturing promises to deliver additional value in the form of less chemical, energy, labor and water usage, as well as fewer pollutants.
Manufacturing waste is generally thought of as any resource used in a production process that does not go out as part of the product and/or costs money to get rid of it (Example: wastewater treatment operations for rinse water). However, manufacturing waste also exists in many other forms: for example, excessive factory space utilization for equipment (production and waste treatment equipment), inefficient material and process flows, inefficient use of facility labor and lost productivity of both labor and equipment. These types of wastes significantly impact a company’s bottom line, too, but are often obscured in overhead accounts or generally overlooked in the manufacturing operation. However, as exemplified in Figure 1, these wastes are real but addressable.
Leading companies in the high tech manufacturing industries are moving beyond just producing high capacity, low-power products.
For example: Seagate Technologies, a hard disk drive manufacturer, is implementing various environmentally protective manufacturing initiatives, summarized on their website. The supply chain in this industry is also implementing cleaner production techniques to reduce energy inputs and product defects. 1 Introduction to CO2 CleanTech. Over the past 25 years, our CO2 clean manufacturing technology (CO2 CleanTech) has been used by many companies in high technology, high reliability, and high capacity manufacturing operations. Industries have included aerospace, hard disk drive, electronics, and optics, among many others. CO2 CleanTech has been used primarily as a means for increasing the cleanliness of components, assemblies, tools and fixtures to increase both capacity and quality. However, arguably more significant, CO2 CleanTech has proven itself to be a means for reducing the cost and improving the productivity of manufacturing high volume and high reliability products. CO2 CleanTech is an effective business sustainability strategy.
CO2 CleanTech offers manufacturers, component suppliers and assembly equipment OEMs new techniques to re-tool their factories and equipment for clean production. Assembly tool builders can develop and deliver clean-in-place assembly process-tool combinations to support sustainable manufacturing initiatives. Component suppliers can produce and supply better quality product at lower cost and device manufacturers can adapt dry clean-in-place capability throughout the factory. CO2 CleanTech can uniquely address the composite opportunity to reduce both lean and green manufacturing waste throughout the production network; tool suppliers, components suppliers and manufacturer.
High tech, high reliability manufacturers require state-of-the-art clean manufacturing technology and implementation strategies for successful design and execution of product quality improvement and manufacturing waste reduction programs. Manufacturing waste reduction programs involving CO2 CleanTech provide a combination of possibilities (and benefits), including:
- CleanTech eliminates or reduces composite forms of manufacturing waste: time, labor, space, transport, defect, inventory, processing, equipment, raw materials, air pollution, water pollution, wastewater, solid wastes, and energy wastes.
- CO2 CleanTech improves quality and reliability requirements imposed by advanced materials, manufacturing methods and processes, and new performance standards.
- CO2 CleanTech integrated into flexible automation, modular and clustered assembly operations (cells) eliminate repetitive operational task errors and reduce skilled labor wastes.
- CO2 CleanTech integrated into tools and processes produces more adaptable and flexible production tools and methodologies which improve efficiency and productivity in high volume or high tech production operations.
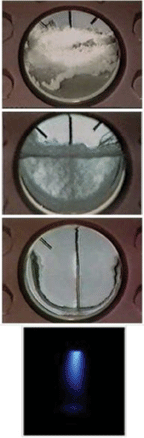
CO2 is a Unique Manufacturing Solution. CO2 is a safe and abundant compound that plays a very important role in many commercial and industrial applications. As described in Figure 3, CO2 can be used in cleaning, cooling and machining applications. Leading companies have implemented CO2-based cleaning technology and have realized improved productivity and a lower cost-of-operation of their production operations. CO2 CleanTech has also served as a strategy for complying with worker safety and environmental regulations. The CO2 used in our cleaning, machining and thermal control products and processes is the same CO2 used to charge fire extinguishers, carbonate beverages, weld steel, cast metals, and refrigerate products, among many other important industrial uses. In fact it’s the same CO2 that you are exhaling while reading this article—approximately 1 kilogram of it every day!
CO2 is an abundant (and recyclable) by-product of numerous industrial and natural processes. Recycled CO2 is a valuable and renewable manufacturing resource that will never run out of supply. Unique benefits derived from using recycled CO2 include the conservation of water, reduced energy consumption and a reduction in industrial CO2 emissions. Moreover CO2-based process technology is a positive contribution to Hazardous Air Pollutant (HAP), Volatile Organic Compound (VOC), and Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emissions reduction strategies.
Using recycled CO2 to reduce pollution, conserve energy and eliminate wastes (both environmental and manufacturing) produces numerous tangible and measurable benefits. Major industrial sources of CO2 emissions include:
- Electrical power generation and usage
- Chemical generation and usage
- Transportation
The use of recycled CO2 technology as a chemical/process substitute lowers electrical power usage, reduces manufacturing wastes, increases manufacturing productivity, and decreases the need for chemicals such as lubricants and solvents, among many other positive socioeconomic and environmental benefits. A reduction of manufacturing wastes or elimination of production chemical inputs of any kind decreases industrial CO2 (carbon) footprint. Following are examples of how this works:
- Less CO2 is produced if less electricity is consumed for processing.
- Less CO2 is produced if less oil is refined, transported and consumed.
- Less CO2 is produced if less cleaning solvents are produced, transported and consumed.
- Less CO2 is produced if more products can be manufactured for the same energy, labor and space inputs.
- Less CO2 is produced if products don’t have to be cleaned using hot deionized water or dried using solvents or other drying agents.
Thus, from a GHG emissions perspective, using recycled CO2 significantly offsets new CO2 gas production and emission from both the industrial supply and consumption sides of the equation. Pending USEPA CO2 emissions reporting legislation is intended to impact the “generators” of CO2. A user of recycled CO2 is not considered a generator of CO2. Note: The CO2 used in commercial and industrial processes is already accounted for in the GHG emissions inventory.
With regards to smog generation, CO2 is not a VOC and is not regulated as such. From a worker health and safety perspective, CO2 is non-toxic. From a building safety and equipment protection perspective, CO2 is non-flammable and non-corrosive. CO2 is a perfect solution for protecting the environment and improving the health and safety of both workers and communities, while improving the performance and cost-of-operation of supplier and manufacturing operations.
CO2 is Many Manufacturing Agents in One. CO2 is a very versatile manufacturing agent—actually four manufacturing agents in 1. It can be used as a spray, immersion solvent, extraction solvent, and plasma in the form of composite sprays, hybrid solid-plasma sprays, centrifugal liquid carbon dioxide cleaning systems, and supercritical fluid extraction systems. In addition, CO2 fluids purification and management systems have been developed to support these various capabilities. CO2-based manufacturing and industrial applications are as diverse. Applications for CO2 CleanTech include precision degreasing, departiculation, outgassing, drying, disinfection, surface modification and functionalization, cooling and lubrication, among many others.
CO2 physical and chemical properties are similar to HFE and CFC solvents such as Freon® 113 and HFE-7100. CO2 possesses a Hildebrand solubility parameter in the adjustable range between 14 MPa1/2 to 22 MPa1/2 depending upon phase, temperature and pressure. CO2 can be compressed to a range of liquid-like densities, yet it will retain the diffusivity of a gas with extremely low viscosity. Supercritical and liquid CO2cleaning agent densities may be adjusted between 0.5 g/cm3 and 0.9 g/cm3. Solid phase CO2 has a density of 1.6 g/cm3, identical to Freon 113. Surface tensions range from 0 dynes/cm (supercritical) to 5 dynes/cm (liquid). Practical benefits derived from these unique properties include rapid penetration and wetting, oil solubility and, cooling and dry lubrication effects. CO2 Technology Reduces or Eliminates Manufacturing Waste. CO2 CleanTech eliminates or significantly reduces waste generation at the production operation level (i.e., at the source) by modifying manufacturing processes, and in particular precision cleaning, assembly processes requiring critical cleaning, and precision machining operations. CO2 modifies conventional manufacturing processes and tools in several dimensions, described as follows;
- Physically; shape, size, space, application and configuration;
- Chemically; solvency, toxicity, and dryness;
- Quality; defects, rework, scrap; and
- Time; productivity.
CO2 CleanTech may be implemented in a variety of production equipment and process configurations to meet the needs of lean production schemes and product flow constraints, including both existing and new production line and tool implementations.
Examples of manufacturing activities that produce manufacturing waste include:
- Moving products off-line or out of cells to clean them and then returning them back to the line or cell
- Filtering and treating spent alkaline cleaning chemistries
- Monitoring cleaning and machining fluid chemistries
- Rinsing parts with deionized water
- Drying parts with compressed air or alcohol
- Treatment and disposal of spent dicing, cleaning and machining agents
- Completing waste hauling manifests
- Preparing environmental reports
- Deionized water treatment
- Rinse water treatment and disposal
- Disposal of spent filters and sludge
Consider how CO2 CleanTech can eliminate many different forms of manufacturing wastes:
- Space and process step reduction: CO2-enabled cleaning processes can reduce multiple processing steps to a single step and perform in less space, sometimes no extra space is needed if the CO2 process is integrated directly into/onto a new or existing manufacturing tool such as a bonder, dispenser, or machining tool.
- Materials selection and productivity: Recycled CO2 itself does not generate waste, does not require environmenta management, and eliminates equipment cleaning and maintenance.
- Energy conservation: Using recycled CO2 eliminates the need for additional energy to heat cleaning baths, dry parts, or evaporate and concentrate wastes.
- Waste reduction and elimination: CO2 does not itself become a waste by-product. CO2 eliminates the wasteful consumption, treatment and disposal of water,wastewater and associated solid wastes.
- Air pollution reduction: CO2 is not considered an air pollutant, is non-toxic and is odorless within the factory atmosphere.
Examples of unique CO2-enabled production configurations and manufacturing waste reduction benefits are summarized in Table 1. CO2 Technology Implementation in the Production Network. CO2 CleanTech can be implemented throughout the production network. Following are some examples and benefits:
- Tool Builders – Production of new, hybrid clean-, cool-, or lubricate-in-place manufacturing tools (Clean-Assembly Tools).
- Component Manufacturers – More profitable operations and cleaner products produced.
- Automation and Robot Suppliers – Integrate robots with CO2 Processor Unit (CPUTM) and assembly technology to provide drop-in-place reconfigurable automated clean assembly solutions.
- Production Line Builders – Integrate CO2 technology into new factories to decrease space, improve product flow and process efficiency.
- Contract Cleaning Service Providers – Utilize CO2 cleaning rather than aqueous or solvent technology for more profitable operations and cleaner products.
- Device Manufacturers – Adapt existing production lines, tools, and processes with CO2 technology to enable cellularity, lean operation and green production.
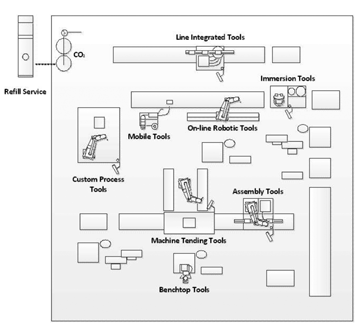
CO2 CleanTech can be integrated into virtually any machine, equipment platform, and process to provide in-situ dry, clean surface treatment, process thermal control and cooling-lubrication. CO2 CleanTech performs these functions without producing air pollution, wastewater or solid wastes, and enhances product yield, tool productivity and increases energy savings.
Following are examples of implementation:
- Mobile tools, including mobile robotic tools
- Production line integrated tools
- Manufacturing tools (Clean-Assembly tools)
- Cellular or island cleaning tools
- Robot-enabled tools, including tenders
- Work bench tools
CO2-enabled cellularity is very productive because two or more value-add manufacturing operations can be performed along with non-value-add dry cleaning, cooling and lubricating within the same work space. Products don’t have to be removed, transported, cleaned and returned, resulting in reduced movement, smaller footprints, less human interaction, higher throughput, and decreased cost-of-assembly. Products stay cleaner with less movement as well.
CO2 CleanTech Transforms Manufacturing. It has been 250 years since carbon dioxide (CO2) was discovered by Joseph Black, about 150 years since the first understanding of CO2’s remarkable chemical properties, and 25 years since our first CO2 precision cleaning applications were developed. Today CO2 CleanTech is being used commercially in many forms throughout industry to address a variety of manufacturing challenges. CO2 CleanTech serves as an alternative to many conventional surface immersion, extraction, spray and plasma cleaning and treatment processes.
Our pioneering work over the past three decades has demonstrated that CO2 CleanTech is uniquely versatile and adaptable to the production of a diverse array of manufactured products ranging from radial tire molds to guidance gyros, automobile fuel injectors to spacecraft materials, and aircraft engines to disk drive components. More recently, CO2 CleanTech has found its way into machining operations as a replacement for flooded coolants, and more specifically to address the higher cutting heat demands of advanced materials such as ceramics, superalloys and composites. CO2 CleanTech transforms manufacturing operations in a variety of ways to provide better, faster, cleaner and cost-effective solutions for many different manufacturing applications.
CO2 CleanTech has been applied in ways not possible using conventional technologies such as aqueous and solvent cleaning technology, and more recently machining coolant technology. This is a quality that portends a transformational technology. A transformational technology changes the “value networks” for the manufacturing industry. Value networks comprise sales and distribution channels, performance standards, suppliers and product and services forms, among other elements. New value networks – the creation of new contexts of consumption and competition – are currently being developed for CO2 CleanTech to realize its full potential throughout the manufacturing industry.
| Equipment and Process Configuration | Waste Reduction Benefits |
| Integrate CO2 CleanTech with automation and environmental control to produce custom stand-alone automated cleaning cells or islands to replace aqueous and solvent cleaners. | Eliminate aqueous cleaning and rinsing fluids, drying equipment and related waste-producing operations. |
| Integrate CO2 CleanTech into existing production lines and processes. | Enables in-line cleaning where none existed and without an increase in floor space. |
| Hybridize CO2 CleanTech with one or more assembly processes such as dispensing, bonding, welding, coating, curing, soldering, and inspection to form clean-assembly cells. | Eliminate the need for separate and additional cleaning equipment, processes and related waste-producing operations. |
| Integrate CO2 CleanTech with machining and metalworking tools to enable minimum quantity cooling lubrication | Improve surface finish – less defects. Eliminate flooded lubrication and follow-on cleaning operations. |
REFERENCES
- Chompu-inwai et al, “Application of Cleaner Technology Concepts in the Arm Coil Assembly Process of Hard Disk Drive Manufacturing”, Proceedings of the International Conference of Engineers and Computer Scientists, 2010, Volume III.
BIO David Jackson (a.k.a The CO2 Guy) is president of CleanLogix LLC and CleanLogix Asia Pte. Ltd. based in California and Singapore, respectively. CleanLogix offers manufacturers, tool builders, and component suppliers a variety of CO2 -based clean manufacturing integration products, CO2 supply and purification equipment, and installation and equipment commissioning services. Over the past 27 years, Jackson has spearheaded the development and commercialization of more than a dozen products utilizing recycled CO2 for cleaning, machining and thermal control applications. He holds a Bachelor’s degree in Chemistry and has been issued more than 30 patents worldwide.





